Data
Points
Direct
Feed
www.insideoutdoor.com www.insideoutdoor.comDirect
Feed
www.insideoutdoor.comOutdoor
Textile
Green
Glossary
Retail
Report
Outdoor
Textile
Green
Glossary
Retail
Report
www.insideoutdoor.comProducts
Section
www.insideoutdoor.comProducts
Section
Inside
Outdoor
|
Winter
2016
68
Buzz words like sustainability,
compostable and cradle-to-grave are
regularly bandied about by authorities
and spin-meisters. Many use terms
interchangeably or incorrectly. So
Inside Outdoor
decided to parse the
greenwash lexicon and take a stab
at a short glossary of definitions. The
following definitions are as organic
as the topics they address. They are
more operative than definitive, with
the underlying subtext being about the
discourse that we hope to continue.
Indeed, these definitions ar “alive,”
and we expect them to evolve as new
standards are set, technologies are
developed and our industry grapples
with the “sustainability” (see below)
of our businesses. A la Wikipedia,
we welcome anyone who would like
to add, change or modify definitions
to submit their insight to
ernest@
bekapublishing.com
.
The Green
Glossary
will continue to appear in
future issues of
IO
.
3P (People, Planet, Profit)
See Triple Bottom Line
Aerosols
Aerosols are solid or liquid nano-
sized particles dispersed within another
gas. Aerosols are of growing interest
among climate scientist researching
climate change. NASA concludes
90 percent of most aerosols are
naturally formed by actions such as
volcanism. The remaining 10 percent are
anthropogenically produced by smog
and coal, natural gas or oil fired-power
generating plants. The effect aerosols
play upon the earth’s climate is not
fully understood. However, it has been
shown aerosols cool the atmosphere
by reflecting or scattering solar radiation
back into space.
Biodegradable
Aerobic decomposition of a
organic matter through the action of
microorganisms or aerobes. There are
no standards for eco-toxicity or length of
time before degrading to biomass and,
in some cases, eco-toxins.
Biodiversity
Biodiversity refers to the multiplicity
of biological organisms within an
interrelated environment. The scale
of biodiversity ranges from the size
of distinct ecosystems to the atomic
molecular level. Anthropogenic climate
change is often cited as a disrupting
influence to biodiversity. The concern
over these disruption centers around
three essential services biodiversity
brings to humanity. These ecosystem
services are provisioning, regulating
and cultural. Provisioning relates to the
loop providing renewable resources
such as food, water and air. Regulating
services maintain equilibrium within the
environment (e.g. population control,
climate feedback loop). The cultural
component refers to the value humanity
places upon the environment.
bluesign standard
Launched in 2000 as an
initiative by Albers Group/Schoeller
Technologies AG, among others, the
bluesign standard is a certification
scheme for textile ecology. Using
OECD’s (Organization for Economic
Cooperation and Development) test
methods for determining the various
ecotoxicological data needed for the
standard, it strengthened its global
marketing and technical reach when
50% of bluesign was purchased by
Société Générale de Surveillance in
2008. SGS’s business model is built
around ocean-going cargo inspection,
raw material testing and testing of
products from exporting companies or
governments worldwide.
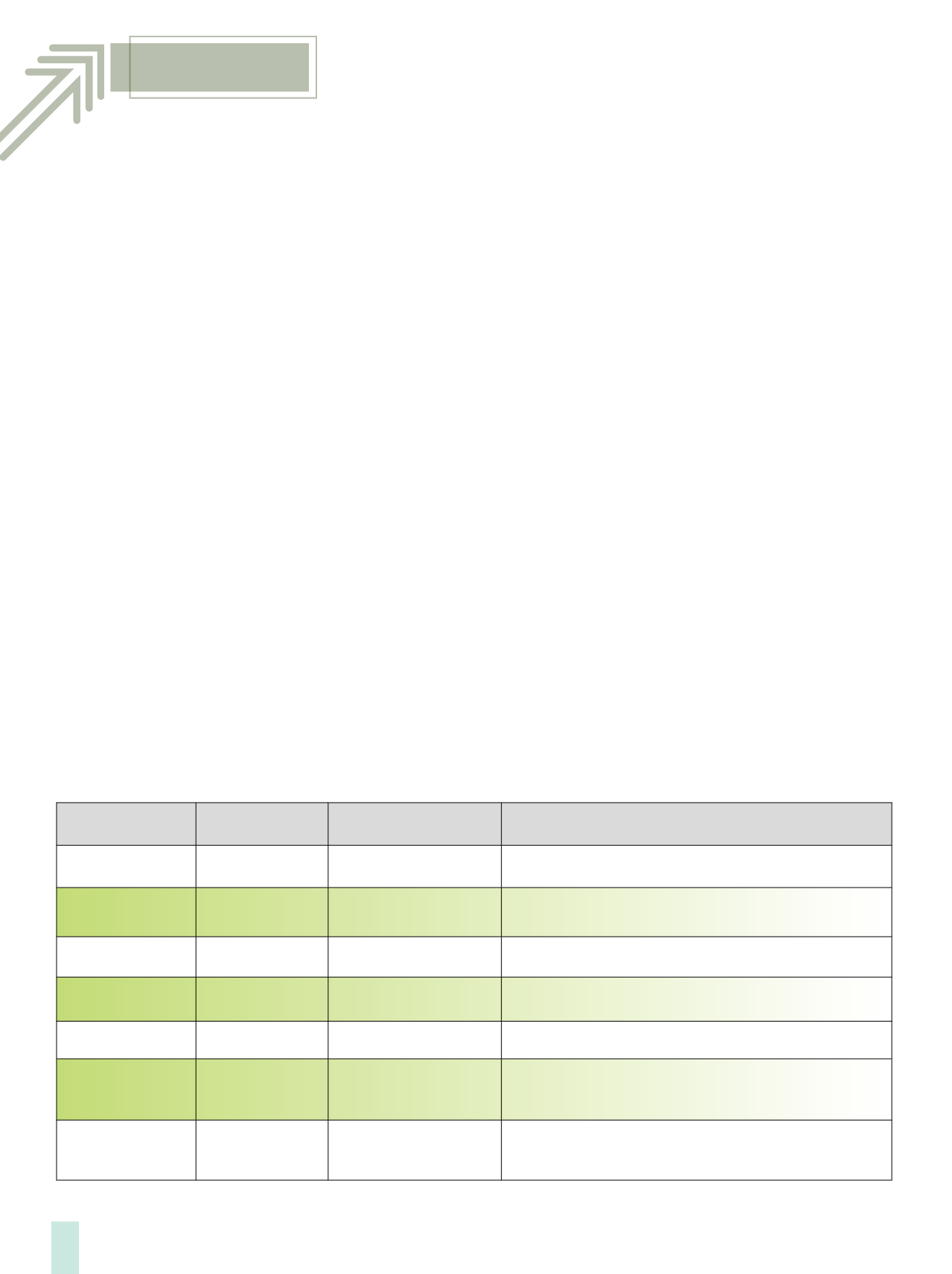
SPI Resin Identification Code
Recycling No.
Abbreviation
Polymer Name
Uses
1PETE or PET
Polyethylene Terephthalate
Recycled to produce polyester fibres, thermoformed sheet, strapping, soft
drink bottles.
2
HDPE
High-Density Polyethylene
Recycled to become various bottles, grocery bags, recycling bins, agricultural
pipe, base cups, car stops, playground equipment and plastic lumber.
3
PVC or V
Polyvinyl Chloride
Recycled to become pipe, fencing and non-food bottles.
4
LDPE
Low-Density Polyethylene
Recycled to become plastic bags, various containers, dispensing bottles, wash
bottles, tubing and various molded laboratory equipment.
5
PP
Polypropylene
Recycled into auto parts and
industrial fibers.6
PS
Polystyrene
Recycled into a wide range of products including office accessories, cafeteria
trays, toys, video cassettes and cases, insulation board and expanded
polystyrene products (e.g. styrofoam).
7
OTHER
Other plastics, including acrylic,
polycarbonate,
polylactic acid,
nylon and fiberglass.
PLA or Polylactic acid plastics at 100% content are compostable in a
biologically active environment in 180 days.
Source: The Society of the Plastics Industry, Inc.